Bend/Twist Constraints 
They are used in rods and bone hierarchies. These constrain the orientation of two particless relative to each other, rotating them to minimize twisting/torsion around the Z axis, and bending around the X and Y axis:
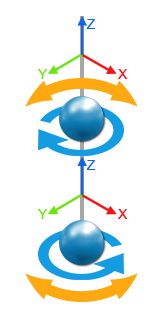
Torsion compliance (m/N)
Amount of torsion allowed along the reference frame's Z axis.
Bend compliance X (m/N)
Amount of bending allowed along the reference frame's X axis.
Bend compliance Y (m/N)
Amount of bending allowed along the reference frame's Y axis.
Plastic yield
Strain threshold that marks the transition from elastic to plastic deformation. Low values will make it easier to permanently deform the constraint. At high values it will take more violent deformation to permanently deform the constraint.
Plastic creep
Once the plastic yield threshold is surpassed, plastic creep determines what percentage of the deformation is permanently absorbed by the constraint.