Emitters
Emitters, as their name implies, emit fluid particles into your scene. They are similar to Unity's built-in particle emitters, but they do not emit regular particles. Instead, they emit Obi particles, which can interact with each other as well as other objects.
To create a emitter, go to GameObject->3DObject->Obi->Obi Emitter.
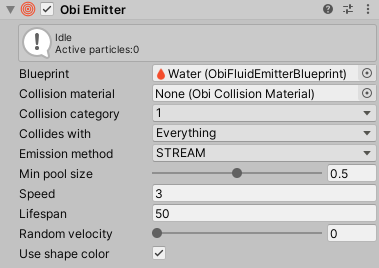
By default, all particles will be emitted from the object's origin. Except for very simple effects, you will want a more complex shape to be used as the source for emitting particles. You can add any of ObiEmitterShape components (square, disk, edge, sphere or image) to any object in your scene, and drag the ObiEmitter component onto its "emitter" property. This will allow the emitter to emit particles trough that particular shape.
ObiEmitters have a lot of parameters that allow you to specify how and when to emit particles:
Blueprint
A reference to an ObiEmitterBlueprint asset. There are two types of emitter blueprint: fluid blueprints, and granular blueprints. This determines the maximum amount of fluid that can this emitter can create as well as its physical properties: you can think of it as the fluid tank feeding the emitter. See emitter blueprints for more info.
Collision Material
Material used to resolve collisions. See collisions.
Collision category
Category used by this emitter's fluid. See collisions.
Collides with
Categories this emitter's fluid is allowed to collide against. See collisions.
Emission method
Emitters can use one of two emission methods:
Min pool size
Minumum amount of particles (as a percentage of the blueprint's capacity) that must be ready for emission before the emitter begins emitting.
Speed
Emission speed. When set to zero, the emission will completely cease. Higher values will cause the emitter to continuously emit fluid at this speed (in meters per second). The amount of particles emitted per second is automatically calculated depending on the fluid resolution and emitter shape size. This ensures that emission is as smooth as possible.
Lifespan
Amount of seconds elapsed between the birth of a particle and its return to the emitter's particle pool.
Random velocity
Amount of random direction applied to the initial velocity of all particles. A setting of 0 will cause particles to be emitted in the direction specified by their current spawn point, while a setting of 1 will cause them to be emitted in a completely random direction.
Use shape color
When enabled, particles will be tinted by the color of the shape they're being emitter from.
Emitter shapes
You can add a emitter shape to any object in the scene. Once you assign an emitter component to the shape, the emitter will begin using it to emit particles. There are a few standard emitter shapes, though you can create custom ones trough scripting if needed:
Disk
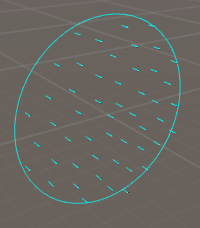
Disk emitter shapes generate particles using a circle defined in their XY plane. Parameters: Color: overall color tint of particles emitted trough this shape. Radius: radius of the circle in local units. Edge emission: if enabled, particles will be emitted from the circle's edges, instead of its interior.
Square
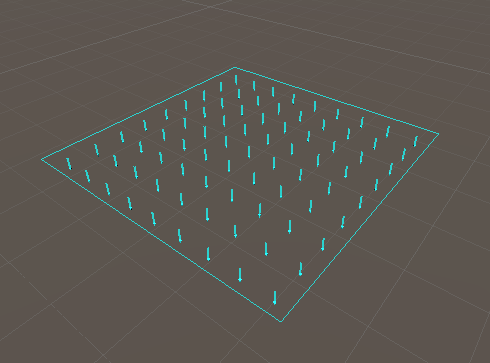
Square emitter shapes generate particles using a square defined in their XY plane. Parameters: Color: overall color tint of particles emitted trough this shape. Size: size of the square in local units.
Edge

Edge emitter shapes generate particles from a line segment defined along their X axis. Parameters: Color: overall color tint of particles emitted trough this shape. Lenght: lenght of the edge in local units. Radial velocity: amount of velocity twisting along the lenght of the edge.
Sphere
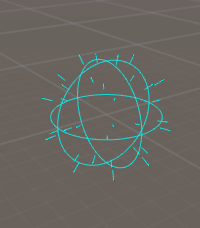
Sphere emitter shapes generate particles from a spherical volume. Parameters: Color: overall color tint of particles emitted trough this shape. Sampling method: Lets you switch between grid-based sampling of the sphere's volume, or regular sampling of its surface. Radius: radius of the sphere in local units.
Cube
Cube emitter shapes generate particles from a rectangular prism. Parameters: Color: overall color tint of particles emitted trough this shape. Sampling method: Lets you switch between grid-based sampling of the sphere's volume, or regular sampling of its surface. Size: size of the prism in local units.
VoxelMesh
Mesh emitter shapes voxelize a mesh and generate particles from each resulting voxel. Parameters: Color: overall color tint of particles emitted trough this shape. Mesh: mesh used for voxel generation. Scale: local scale of the mesh.